
The difference between SSD, M.2, and NVMe hard drives, and what is the appropriate use for each storage unit?
SSDs appear as an ideal solution that combines high performance with technical benefits. In the era of technological development, the pace of computer use is accelerating and there is an increasing need to increase the speed of devices and expand file storage capabilities as well as obtain a smoother user experience compared to traditional technologies such as HDDs. In this context, we will examine the main differences between SSDs and other advanced storage interfaces such as M.2 and NVMe. We also highlight the advantages of each technology to help you make the best decision when upgrading or purchasing a new storage unit, and ensure that you take full advantage of your device’s capabilities.
Is there a difference between SSD, M.2 and NVMe?
Of course, there are big differences, the most important of which is the speed of writing and reading, but each hard disk or storage unit has a different use that makes it stand out from others in that point.
SDD hard drive:
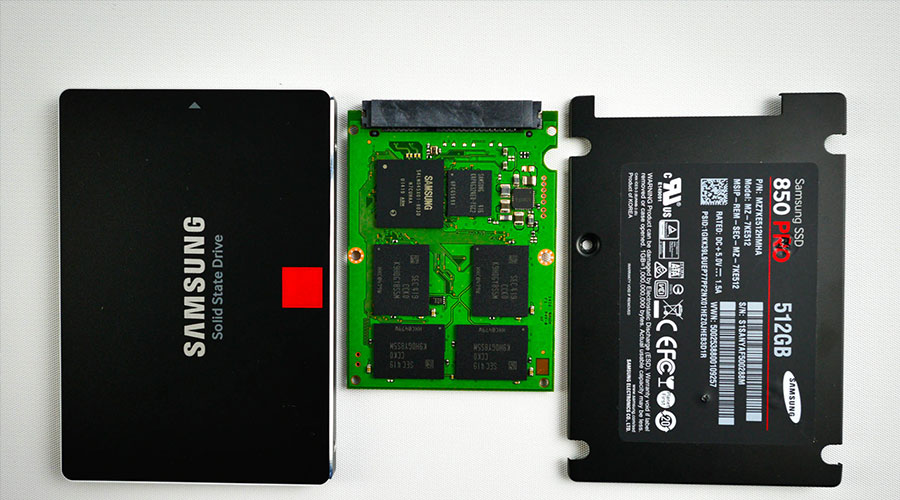

Solid State Drive is abbreviated as SDD, which means non-mechanical hard disk, and this point is what distinguishes it as it consists of electronic chips only without any rotating disk like an HDD hard disk, which makes the reading and writing speed much faster, and also better data protection due to the absence of moving parts that can be damaged for many reasons, and the chips used in the SSD hard disk are called NAND Flash, and thanks to these chips the hard disk speed reaches large numbers, but at a higher cost of course, and it should be noted that the speeds differ from one SSD hard disk to another and from one manufacturer to another, and each hard disk has a different price, and the highest speed for an SSD hard disk: comes from Samsung, which is the Samsung 870 Pro with a speed of 550 megabytes per second for reading and 520 for writing, i.e. copying.
M.2 hard drive:
The M.2 form factor, formerly known as the Next Generation Form Factor or NGFF, represents a paradigm shift in internal storage technology. It replaces the previous mSATA (Mini-SATA) standard, and offers significant performance and connectivity benefits. It differs from standard hard drives and drives primarily in the way they are connected. While standard drives require a cable to connect them to the motherboard, M.2 modules are connected directly to the motherboard using a dedicated M.2 connector slot. This design makes the internal computer cleaner and less cluttered with cables.
M.2 drives can take advantage of either the standard SATA interface or the faster PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, and are connected directly to the motherboard. In most cases, M.2 is used to store SSD data, making it an effective alternative to existing 2.5-inch storage drives that are connected to the motherboard via a SATA cable. Some computer peripherals, such as Wi-Fi cards, can use M.2. However, using M.2 to store SSD data is still the most common use. If you're looking for high speeds, it's a good idea to check out the NVMe interface with M.2 for superior performance.
NVMe hard drive:
The acronym NVMe stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, and refers to the method of transferring data rather than the physical form of the drive. NVMe relies primarily on the PCIe interface to access the motherboard, which ensures data transfer speeds much higher than the current SATA standard. NVMe drives can be five or six times faster than traditional SATA drives. Some NVMe drives are available in a design that fits into a standard PCIe motherboard slot, such as graphics cards.
However, most NVMe drives use the M.2 form factor. Additionally, due to their superior speed, NVMe drives are typically priced higher than their SATA-based equivalents. The cost differential also means that NVMe drives are often more expensive than a 2.5-inch SSD just as it is between hard drives and mechanical drives for the same storage volume.
When looking at performance, it is noted that the speed gain offered by the NVMe protocol is mainly evident in sequential read and write operations, while the difference is small when dealing with random read and write operations. Therefore, the full benefit of NVMe is most evident when using the computer for demanding tasks such as editing high-resolution video or transferring large amounts of data regularly. In terms of compatibility, it is preferable to check the motherboard’s support for M.2 slots and the type of protocol it supports (SATA or NVMe).
What is the difference between NVMe and M.2?
The main difference between NVMe and M.2 is the interface and performance. M.2 is the form factor, while NVMe refers to the way data is transferred. When looking at modern motherboards, we find that they have a SATA 3.0 port that provides a maximum speed of up to 600 MB/s. An SSD hard drive connects to a SATA port to achieve speeds ranging from 500 to 550 MB/s, which is a significant improvement over a traditional HDD hard drive. An NVMe hard drive uses the same M.2 port, but it is distinguished by its ability to communicate with the motherboard at a higher speed. It is characterized by amazing data transfer speeds, as it can reach five or six times faster than a regular M.2 hard drive that relies on SATA.
Not all M.2 drives are NVMe, as they can come in versions that use the SATA interface, so it is important to consider the type of interface used. While NVMe M.2 allows you to benefit from the highest transfer speeds, regular M.2 with SATA is a less expensive option but offers good performance for everyday uses. In short, NVMe M.2 is the best choice for those who want maximum performance for specific applications such as high-resolution video editing, while M.2 with SATA can meet the needs of everyday uses effectively and at a lower cost.
What is the difference between SSD and M.2 NVMe?
- M.2 NVMe technology is more advanced in performance than SSD hard drives, as M.2 NVMe technology takes advantage of the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, which improves read and write speeds.
- SSDs typically come in standard 2.5-inch drives, while M.2 NVMe comes in smaller, plug-in-like units.
- SSDs work efficiently on most modern computers, while M.2 NVMe requires support from the motherboard and operating system to function efficiently.
- Although M.2 NVMe is superior in performance, the difference in everyday use is often not noticeable, except for special tasks like video editing or heavy gaming, where M.2 NVMe may be the better choice.
- The SSD relies on SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) interfaces, which are slightly slower than the PCIe interface used in M.2 NVMe, and requires the SSD to be connected to a SATA port, while M.2 NVMe is connected directly to the M.2 port on the motherboard.
- In general, consider the total cost of what you will buy based on your usage. If you use your device for browsing, watching movies, and other light things, then choosing an SSD hard drive for the system with a capacity of 120GB or 200GB is an excellent choice, and next to it an HDD for storing files and the like. If you use it for editing and content creation and you need speed, then buying NVMe is advisable because you will need it a lot.
Comparison of HDD\SSD\M.2 storage unit speeds:
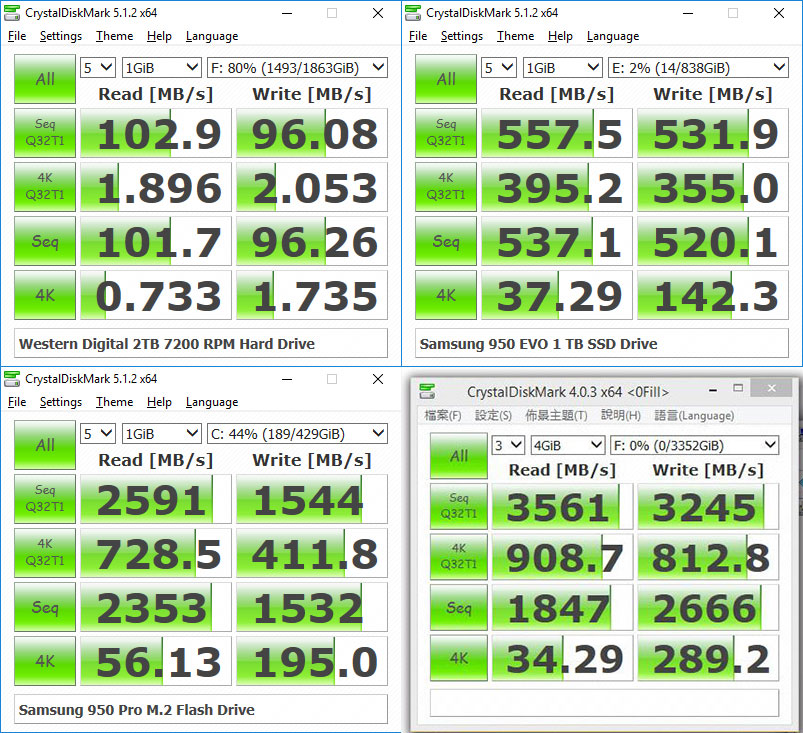
Of course, you need a good processor and at least 16 GB of RAM to get those speeds. When comparing the speed of NVMe with SATA, the big difference in data transfer performance becomes apparent. Modern motherboards use the SATA III port , which provides a maximum speed of up to 600 MB/s, and most regular SSDs rely on this connection, offering read/write speeds ranging between 530 and 500 MB/s, respectively.
In contrast, NVMe hard drives come with impressive performance, with write speeds reaching 3500MB/s for Gen 3 and up to 5000MB/s for Gen 4. This means that NVMe offers much faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs, reaching 7 times for Gen 3 and up to 35 times for Gen 4. Accordingly, as we mentioned earlier, if your applications require high performance on the drive or include intensive read/write operations, NVMe is the best choice, and given the low prices of this technology, moving to it may be a advisable option.
Read also: Best Storage Cloning Apps on Windows 11
