How to erase and format a drive in Windows
Did you get a new external drive? Or are you looking to troubleshoot or sell your old drive? After that, it is good to erase and initialize them. Read on to find out how to do this in Microsoft Windows 10 and 11.
When you buy an external hard drive, SSD (solid-state drive) or flash drive, it is likely that you can connect it to your Windows personal computer and use it immediately. However, you may still want to erase and format the drive, so that you know that you are starting with a clean registry and a proper file system.
If you've already been using the drive for some time, formatting can help resolve ongoing performance issues and other issues. You should also reformat the drive and safely erase its data if you plan to sell it.
How drive scanning and formatting work in Windows
When you format an external hard drive, SSD, or USB flash drive in Windows, the operating system frees up disk space to be used by other data. In addition, reliability checks are performed on the drive sectors and serious bug fixes (although there is no guarantee).
But that's just half the picture. The format also gives you the perfect opportunity to implement a suitable file system. This is necessary when you want to make sure that the drive is compatible with other devices. Windows allows you to format external drives using one of the three file systems below.
NTFS: The default Windows file system. NTFS supports large file sizes and provides excellent security, but it doesn't fully work on alternative operating systems besides Windows and Linux.
FAT32 : Old Windows file system. Unlike NTFS, FAT32 has wider compatibility with most operating systems but imposes file size limits of 4GB or less, which is less reliable and insecure.
exFAT: A comprehensive file system that works well on both Windows and Apple macOS for Mac, and exFAT achieves an excellent balance between compatibility, usability, and security.
You can format a drive via the Format utility, the Disk Management console, and the Windows command prompt. However, only a command prompt allows you to execute FAT32 as a file system on drives exceeding 32GB.
However, formatting the drive in Windows doesn't completely erase your data. If you intend to sell the drive, you should use a third-party formatting tool such as Disk Wipe that can securely delete all data. If you're troubleshooting problems on a drive, you might want to consider running Check Disk (CHKDSK) before you start.
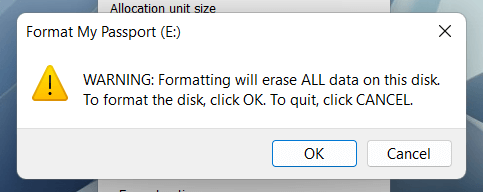
WARNING: Erasing drive or partition will permanently delete all files and folders. Take a backup of any data if you want to restore everything afterwards.
Erase and format a drive in Windows with Formatting Tool
The Format utility, which you can access via File Explorer, is the most convenient way to erase and format external drives in Windows. You can also decide if you want to speed things up by doing a quick format.
1. Open File Explorer and go to the This PC tab on the sidebar. Next, right-click on the external hard drive, SSD or flash drive you want to format and select Format from the drop-down list.
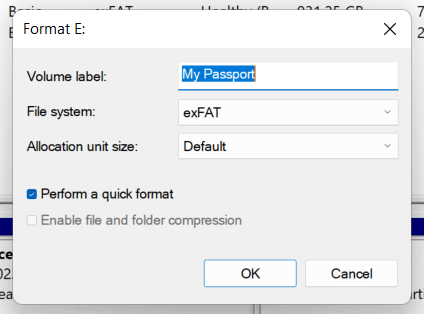
2. Adjust the following settings in the Format dialog box:
File system : Switch between NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT file systems. FAT32 is not available for drives exceeding 32GB.
Allocation Unit Size: Specify the minimum unit size for each data block on your drive. The default selection changes depending on the file system you select - for example, 128 KB for exFAT. Learn more about the size of the customization unit.
Volume label: Replace the default name if you want to have an easier time selecting the drive than other external media. The custom volume label will also appear on other devices and operating systems.
Quick format : Leave the box checked if you want to quickly erase and format the drive. Clear them if you are troubleshooting the drive.
Note: Select the Restore device defaults button if you want to revert to the drive defaults.
3. Select Start > OK. This should be done in seconds if you choose the Quick Format option.
Erase and format drive in Windows using Disk Management
The Disk Management Console is a versatile utility that allows you to manage drives, volumes, and partitions in Windows. It also allows you to quickly format drives. Use it if an external drive fails to appear in File Explorer.
1. Press Windows key + R to open the Run box. Then type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
2. Right click the drive under the Volumes section and select Format button.
3. Add a volume label, choose a file system, and specify the allocation unit size. In addition, uncheck the box next to Make a quick format as is if you want Disk Management to perform full formatting. Then select OK.
Note: If you are formatting a drive with NTFS file system, you can check the box next to Enable compression of files and folders to compress the files and folders you add by default. However, this can negatively affect performance.
4. Select OK again to confirm.
Erase and format drive in Windows using Command Prompt
Alternatively, you can use the command prompt and Windows PowerShell consoles to format a drive in Windows. It is the best option if you want to format drives that exceed 32GB natively in FAT32.
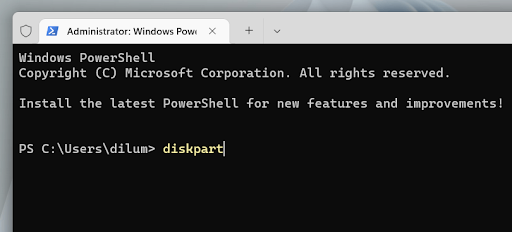
1. Open the Start menu, type cmd, and select Open as administrator to open the Command Prompt console. If you prefer Windows PowerShell, right-click the Start button and select Windows PowerShell (administrator) or Windows Terminal (administrator).
2. Run the diskpart command to load the DiskPart command-line tool.
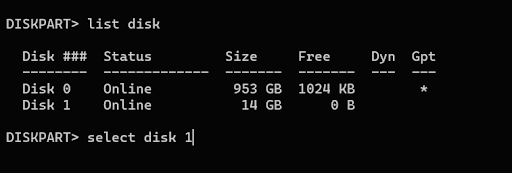
3. Run the list disk command to mount a list of drives on your computer.
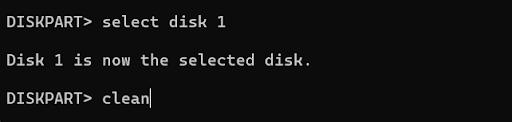
4. Type select disk [disk number], replacing [disk number] with the drive number you want to format. Use the Size column to select the correct number. Press Enter to select the drive.
5. Run the clean command to erase all the data on the drive.
6. Type create primary partition and press Enter to partition the drive.
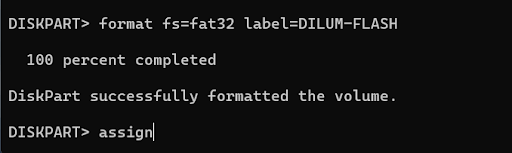
7. Type the format fs = fat32 label = [drive name] . Replace FAT32 with the file system you want and replace [drive name] with a drive label. Then press Enter.
8. Type Assign and press Enter to assign a drive letter to the drive.
9. Type exit and press Enter to exit DiskPart.
Safely erase and format drive in Windows with Disk Wipe
If you want to safely erase an external drive, you can use a free third-party formatting tool called Disk Wipe. It allows you to run different erasing patterns to prevent file recovery tools from retrieving your data.
1. Download and launch Disk Wipe . Then choose the drive you want to format and select the Erase Disk button.
2. Select a file system - NTFS, FAT or FAT32. Then select Next.
3. Select the scan pattern. For example, you can overwrite the contents of a storage device with one pass of zeros or use sophisticated data erasing techniques such as the Peter Guttman method. Note that using multi-pass methods may take a long time to complete.
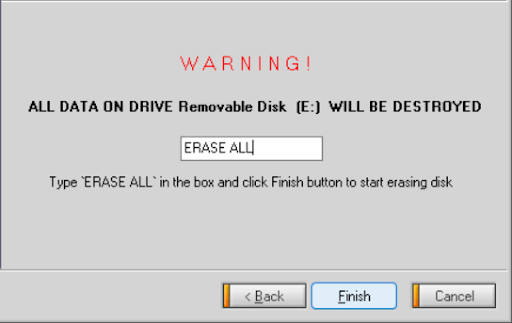
4. Type "Clear All" and select "Finish".
5. Select Yes to confirm.
And apart from Disk Wipe, you can rely on many other formatting tools and apps like DBan, KillDisk, and Eraser to safely erase drives. Here is a complete list of freeware that can scan the entire drive in Windows .