12 basic functions in Excel that everyone should know
Microsoft Excel has many functions that allow you to perform tasks without a calculator or overtime. But if you're not familiar with formulas, you may feel scared. Here, we have listed 12 simple but useful Excel functions to get you started.
1. Add numbers in cells: SUM
One of the most basic things you can do with numbers is to add them. With the SUM function in Excel, you can add numbers in cells.
The syntax is SUM(value1, value2,...) The desired value1 place is value2 and is optional. So for each argument, you can use a number, cell reference or cell range.
For example, to add numbers in cells A2 to A10, you can enter the following and press Enter:
SUM(A2:A10)=
Then you get the result in the cell containing the formula.
2. Average numbers in cells: average
Calculating the average of a set of numbers is another common mathematical function.
The syntax is the same for the AVERAGE function in Excel as with the SUM function, AVERAGE(value1, value2,...) With value1 required value2 and optional. You can enter cell references or range of arguments.
To average numbers in cells A2 to A10, you can enter the following formula and press Enter:
AVERAGE(A2:A10)=Then you get the average in the cell containing the formula.
3. Find the high or low value: MIN and MAX
When you need to find the minimum or maximum value in a range of cells, you use the MIN and MAX functions.
Statements for these functions are the same as others, MIN(value1, value2,...) and MAX(value1, value2,...) with the required value1 and optional value2.
To find the minimum, and lowest value, in a range of cells, enter the following with replacing the cell references with your own references. Then press Enter:
MIN(B2:B10)=And to find the maximum and maximum value, use:
MAX (B2: B10)= You will then see the smallest or largest value in the cell containing the formula.
4. Find the middle value: MEDIAN
Instead of a minimum or maximum value, you may want the middle value.
As you may have guessed, the syntax is the same, MEDIAN(VALUE1, VALUE2,...) With the first argument required and the second optional.
For the middle value in a range of cells, enter the following and press Enter:
MEDIAN (A2: A10)=5. Count cells containing numbers: COUNT
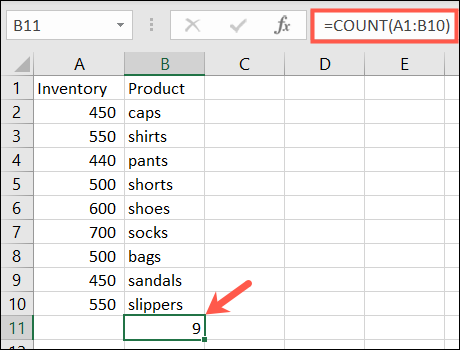
You may want to count the number of cells in the range that contain numbers. For this, you can use the counting function.
The syntax is the same as the two functions mentioned above, COUNT(value1, value2,...) With the first argument required and the second optional.
To count the number of cells with numbers in the range A1 to B10, enter the following and press Enter:
COUNT (A1: B10)= 6. Enter the current date and time: Now
If you want to display the current date and time whenever you open the spreadsheet, use the NOW function in Excel.
The reason for the NOW() syntax is because the function does not have required arguments. However, you can add or remove the current date and time if you like.
To return the current date and time, enter the following and press Enter:
NOW()=
To return the future five days date and time from the current date and time, enter this formula and press Enter:
NOW()+5=
7. Round to a certain number of numbers: ROUND
If you have decimal numbers in the sheet and want to round them up or down, use the ROUND function in Excel.
The syntax is ROUND(value1, digits)where both arguments are required. For value1, use the number you want to round. For digits, use the number of decimal places to round the number.
For example, to round the number 2.25 to one decimal place, enter the following and press Enter:
ROUND (2.25،1)= And you have your results. If you want to round down, just use a negative number for the number argument.
8. Truncate a number by removing the fraction: TRUNC
You may prefer to truncate a number instead of rounding it. Using the TRUNC function, you can remove the fraction from the number.
The syntax of TRUNC(value1, digits) with the required value1 and optional digits. If you do not enter the numbers, the default value is zero.
So, to truncate the number 7.2, enter the following and press Enter:
TRUNC (7.2)=9. Find the product by multiplying the cells: PRODUCT
If you need to multiply multiple cells, using the PRODUCT function is more efficient than using the multiplication symbol (*) in a formula.
Syntax PRODUCT(value1, value2,...) with the required value1 and optional value2. You can use the value1 range of cells value2 and an additional cell range if necessary.
To find the product of cells A2 to A10, enter the following and press Enter:
PRODUCT(A2:A10)=
As you can see, this is much simpler than entering A2*A3*A4, and so on.
10. Use the reference number of a specific cell: column and row
With the COLUMN and ROW functions in Excel, you can return the cell position number. These functions are useful for entering a series of reference numbers in the sheet, or row numbers, for example.
The syntax for each and COLUMN(reference) and ROW(reference) where an argument is not required. If you don't enter an argument, the formula returns the cell reference containing the formula.
For example, if you enter the following formula into cell B2, the result will be 2 because B2 is in the second row.
ROW ()= But if you enter the following formula with an argument, you will receive the cell reference number.
ROW (C5)=You can see here. The result is 5 because C5 is in the fifth row.
11. Eliminate White Space: TRIM
Often when you paste or import data, it contains extra spaces. The Trim function eliminates white space.
The TRIM(reference) syntax with the required argument for the cell reference that contains the data.
To remove extra spaces from cell A1, enter the following and press Enter:
TRIM (A1)= 12. Count the number of characters in a string: LEN
Maybe you need to find the number of characters in a text string. Here, you can use the LEN function in Excel.
LEN(reference) syntax with the required argument for the cell reference that contains the text.
To find the number of characters in cell A1, enter the following formula and press Enter:
LEN(A1)=The result is 25 because the "data usage of finances" contains this number of characters and note that spaces and characters are calculated.
There are many other useful functions in Excel such as VLOOKUP to find a value and CONCATENATE to join text strings. But this list of basics should help you with simple tasks as you become more familiar with using functions.